
摘要
现实世界中的多智能体设置通常涉及具有不同类型和数量的智能体和非智能体实体的任务;然而,在这些智能体/实体中经常会出现共同的行为模式。我们的方法旨在通过提出以下问题来利用这些共性:“当只考虑随机选择的观察实体子组时,每个代理的预期效用是多少?”通过提出这个反事实问题,我们可以识别我们在另一项任务中可能遇到的实体子组中的状态-动作轨迹,并使用我们在该任务中学到的知识来为我们在当前任务中的预测提供信息。然后,考虑到这些不相交的实体组,我们将完整回报的预测重建为因素的组合,并训练这个“随机分解”价值函数作为基于价值的多智能体强化学习的辅助目标。通过这样做,我们的模型可以识别并利用任务之间的相似性来提高多任务设置中的学习效率。我们的方法,随机实体因式分解进行想象学习(REFIL),在具有挑战性的多任务星际争霸微观管理设置中,以显着优势优于所有强基线。
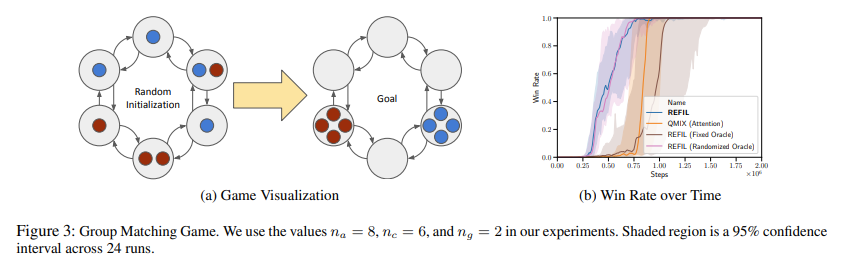
实验环境: soccer
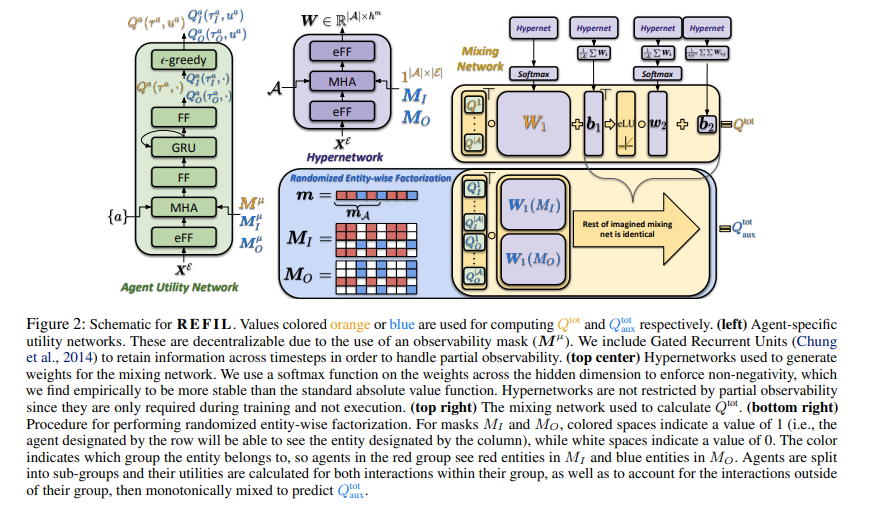
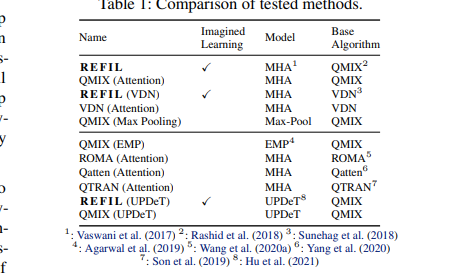
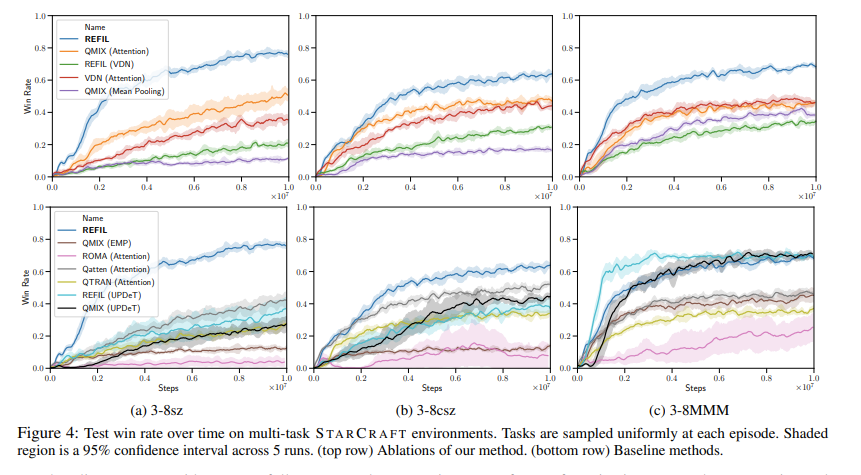
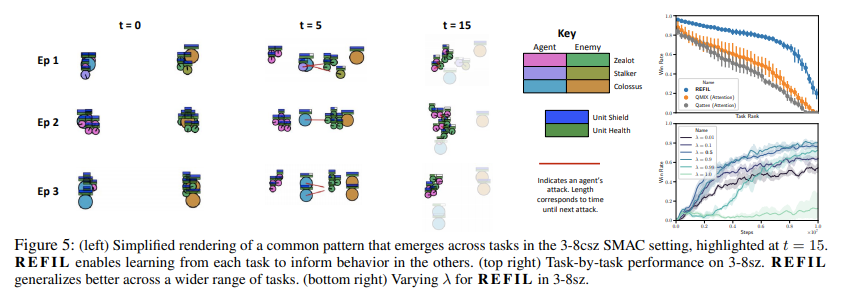
原理图
代码
Dependencies
- Docker
- NVIDIA-Docker (if you want to use GPUs)
Run an experiment
Run an ALGORITHM from the folder src/config/algs in an ENVIRONMENT from the folder src/config/envs on a specific GPU using some PARAMETERS:
./run.sh <GPU> src/main.py --env-config=<ENVIRONMENT> --config=<ALGORITHM> with <PARAMETERS>
引用论文
@InProceedings{iqbal2021refil,
title={Randomized Entity-wise Factorization for Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning},
author={Iqbal, Shariq and de Witt, Christian A Schroeder and Peng, Bei and B{\"o}hmer, Wendelin and Whiteson, Shimon and Sha, Fei},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning},
year = {2021},
series = {Proceedings of Machine Learning Research},
publisher = {PMLR},
}